Standardization and Classification of Capsule Sizes
Capsules come in various sizes, each designed to hold different quantities of active pharmaceutical ingredients
(APIs) and excipients. Standardization and classification of capsule sizes ensure uniformity in the pharmaceutical
industry, making it easier for manufacturers and healthcare professionals to prescribe and dispense medications.
Standardization of Capsule Sizes
Capsule sizes are standardized by organizations such as the United States Pharmacopeia (USP), the European
Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.), and other national pharmacopoeias. These pharmacopoeias establish guidelines for capsule dimensions, filling capacity, and tolerances, ensuring that capsules produced by different manufacturers are
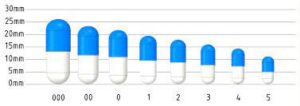
interchangeable and meet specific quality standards. The standardized capsule sizes are represented by numerical
codes, with each code corresponding to a specific capsule size.
Classification of Capsule Sizes
Capsules are classified into different sizes based on their capacity to hold the API and other excipients. The
classification typically includes two parts: a numerical designation and a letter suffix. The numerical designation
represents the overall size of the capsule, while the letter suffix indicates the specific part of the capsule,
either the cap or the body. The most commonly used capsule sizes are classified as follows:
1. Capsule Size Classification Example: “Size 00”
- Numerical Designation: The numerical designation indicates the overall size of the capsule. In
this example, “00” represents a larger capsule size. - Letter Suffix: The letter suffix, when present, indicates whether the size refers to the cap or
the body of the capsule. For example, “00E” refers to the size of the capsule body, while “00EL” refers to the
size of the capsule cap.
Factors Influencing Capsule Size Selection
When selecting a specific capsule size for a pharmaceutical formulation, several factors are considered:
- Drug Dosage: The quantity of the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) and excipients to be
included in each capsule affects the choice of capsule size. Smaller quantities may use smaller capsule sizes,
while larger doses may require larger capsules. - Patient Acceptability: The ease of swallowing and patient acceptability can be influenced by the
size of the capsule. Smaller capsules may be more comfortable for some patients, while others may prefer larger capsules. - Formulation Properties: The physical properties of the formulation, such as density and flow
characteristics, may influence the capsule size selection. - Desired Release Profile: The release profile of the drug, such as immediate release or extended
release, may impact the choice of capsule size and the need for specialized capsule types.
Conclusion
Capsule sizes are standardized and classified to ensure consistency and interchangeability across the pharmaceutical
industry. The numerical codes and letter suffixes provide a clear system for designating capsule sizes, making it
easier for manufacturers, healthcare professionals, and patients to identify and use the appropriate capsules for
specific medications and dosages.